Research
Deep generative modeling for brain MRI harmonization
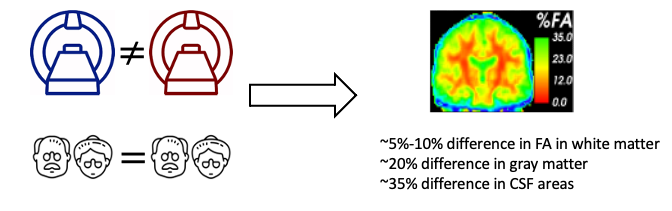
There is significant interest in pooling magnetic resonance image (MRI) data from multiple datasets to enable mega-analysis. Harmonization is typically performed to reduce heterogeneity when pooling MRI data across datasets. We are focusing on developing state-of-the-art deep learning algorithms (e.g., Variational Auto Encoder) to reduce the unwanted dataset differences across datasets. Related studies have been published in NeuroImage and Medical Image Analysis.
Transfer learning for brain imaging based behavior prediction
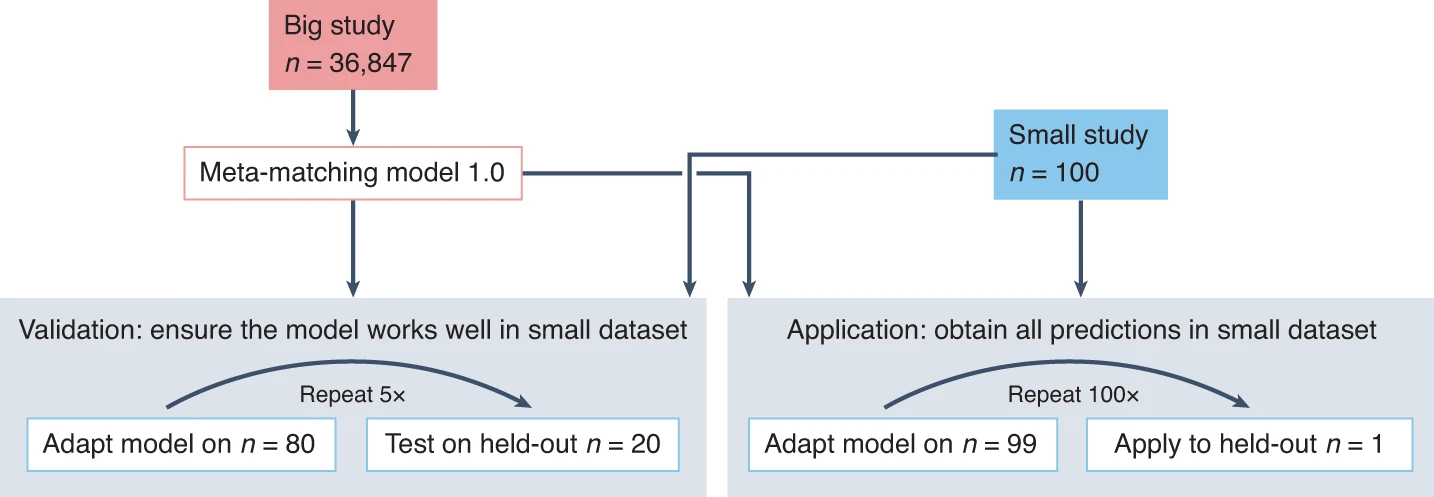
Individual-level prediction is a fundamental goal in systems neuroscience and is important for precision medicine. Therefore, there is growing interest in leveraging brain imaging data to predict non-brain-imaging phenotypes (e.g., fluid intelligence or clinical outcomes) in individual participants. We are focusing on developing machine learning algorithms to help boost the prediction performance on small sample-size datasets. Related studies have been published in Nature Neuroscience and Imaging Neuroscience (x2), and Science Advances.
Disease progression modeling for Alzheimer's Disease
Early identification of people at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (AD) would be beneficial for developing treatments. Utilizing multiple biomarkers such as brain imaging, cognitive tests, we are developing deep learning models (e.g., Recurrent Neural Network, Transformer) to model the progression of Alzheimer's Disease. Related studies have been published in NeuroImage.

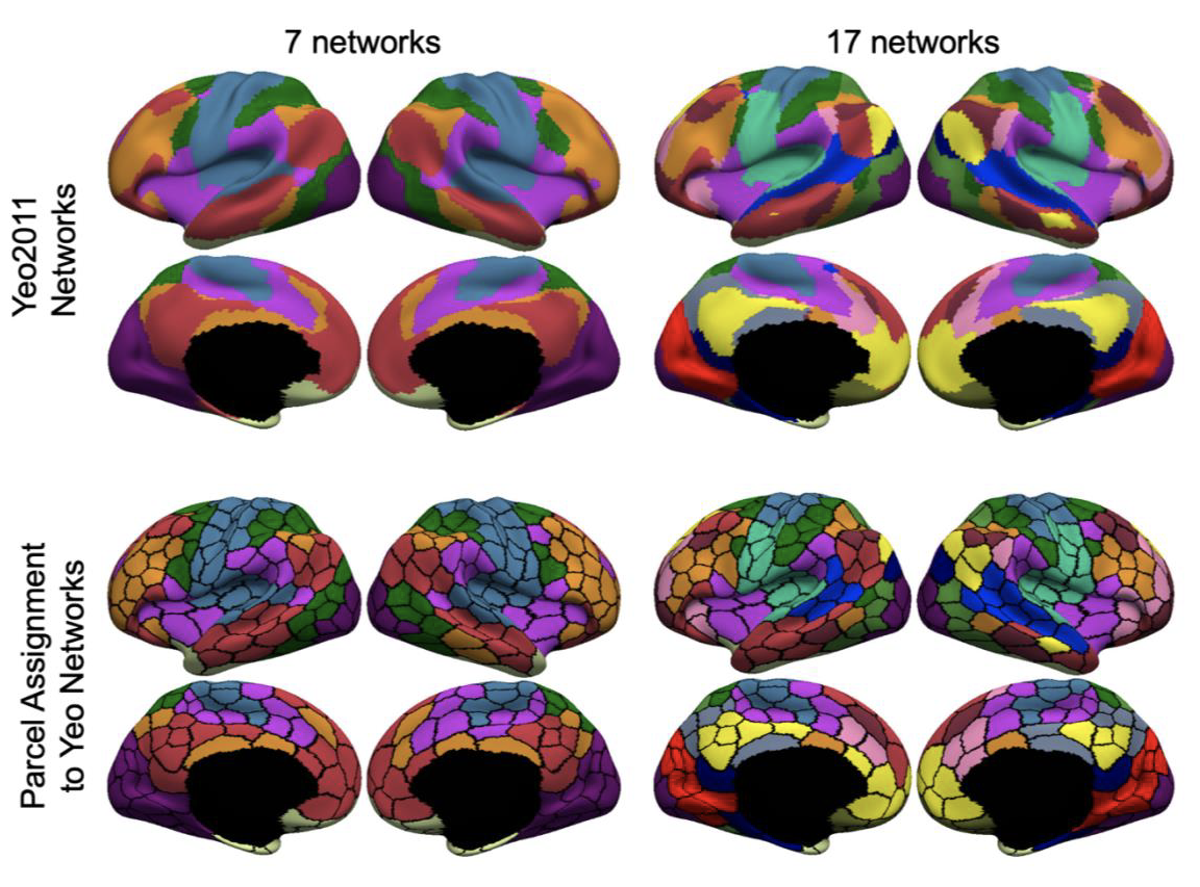
In-vivo delineation of human brain networks and areas
Information processing occurs via transforming neural signals across brain networks. Resting fMRI is a powerful tool allowing the non-invasive, simultaneous, interrogation of multiple brain networks in living individuals. We have utilized resting-fMRI to generate canonical parcellations of the cerebral cortex, cerebellum and striatum into distributed large-scale networks. Releated studies have been publised in NeuroImage.